Customers are the primary focus of any successful business, and smartbilling focuses on customers as the key and most important element of the system, located directly at the left of the navigation pane. This functionality will be used by Operations, Customer Service, Sales, Administration and during Implementation. This User Interface (UI) screen allows users to configure and populate the information fields that describe the customer, manage the customer account, contacts locations, miscellaneous charges and products, subscriptions, and to search for and display the elements within the customer.
¶ Accounts
The navigation on the Customer Account List View screen is rich. The UI screen has two search boxes: (1) a ‘global’ search bar that does a general search within the entire SmartBilling database, and (2) a ‘local’ search bar that is limited to the displayed list of accounts.
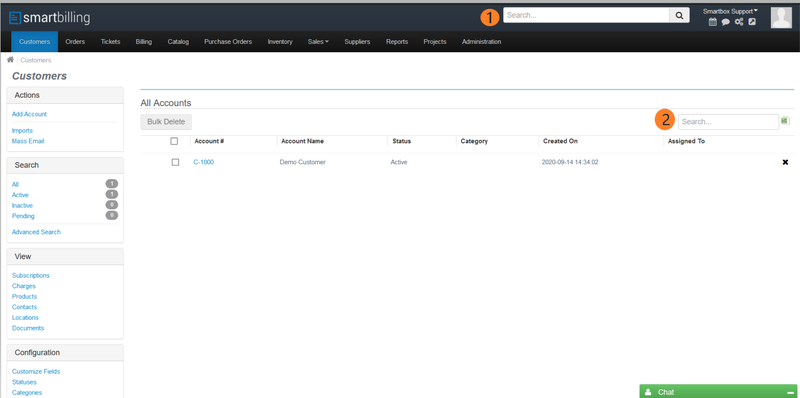
Within the displayed list, you can view individual customers by clicking on the blue Account # values; you can also delete customers if no transactions have been created for them (e.g. posted invoices, payments, credit notes, etc.) by clicking the x icon to the right of the account row.
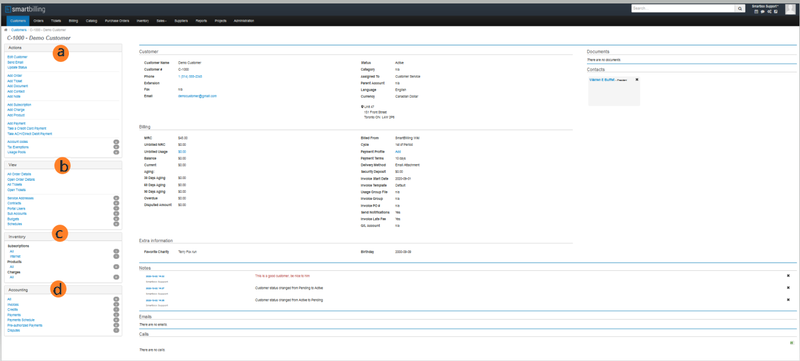
You can also configure the account information that you collect and store by adding custom fields. smartbilling adapts to your business needs and allows you to add custom fields to most objects that smartbilling defines. You can configure the accounts fields that are important for your business and manage them.
Let´s look at the demographic information for the customer and the most important functionalities starting with the Customer Configuration Account Info, Add & Import, Configuration, Mass Email and Contact, Locations and Document.
¶ Subscriptions
A subscription is an object that represents a series of Products, Charges, and Usage Rates which the company that have been contracted with a customer. Charges for these items can be One-Time, recurring (repeating on a regular (monthly, quarterly, etc.)) basis, or Consumption-dependent (Usage Rate)
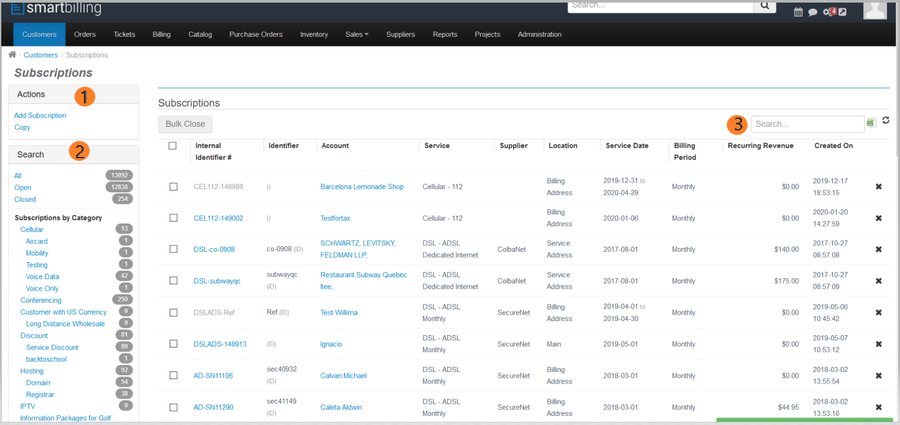
Smartbilling provides all possible features needed in the subscription economy. The supplier field will allow you to reconcile in the future revenues vs costs at subscription level, for that data is captured in the process. You can add, delete and copy subscriptions (1), and you can manage the subscription or your customer service team can modify or add new services to a subscription. The Search Categories box (2) contains category filters that work in conjunction with the Search Filter box (3) allow users to narrow the list of subscriptions to match the search criteria. Clicking on a column heading will sort the list in ascending order by the values in that column; clicking a second time will sort in descending order; clicking a third time will revert to the original list order.
In the screen shot below, please take note that subscriptions whose identifier has been greyed out have been ‘closed’ – in other words, an Effective-To date has been included specifying when the subscription should end. (After which the charges will no longer be invoiced.)
Subscriptions can only be associated with a single service. If multiple services are provided, each service will be tied to a single subscription. A subscription can contain multiple Products, Charges, Sub Charges and usage rates (2).
Subscriptions can also be linked to one or more non-overlapping ‘Contracts’. A Contract indicates that the customer has received special pricing in return for a commitment to maintain the subscription for a specified term. Often, if a customer terminates a subscription prior to the term currently in force, penalties may apply in order to cancel the contract.
A Subscription need not be comprised only of mandatory charges relating to the Service provided. It can include additional optional Miscellaneous Products(2) and Charges(3) that are provided in conjunction with the Service. Products and Charges include a Primary Price/Cost (which could be offered for free), but can also be associated with multiple sub-charges which can apply in particular situations.
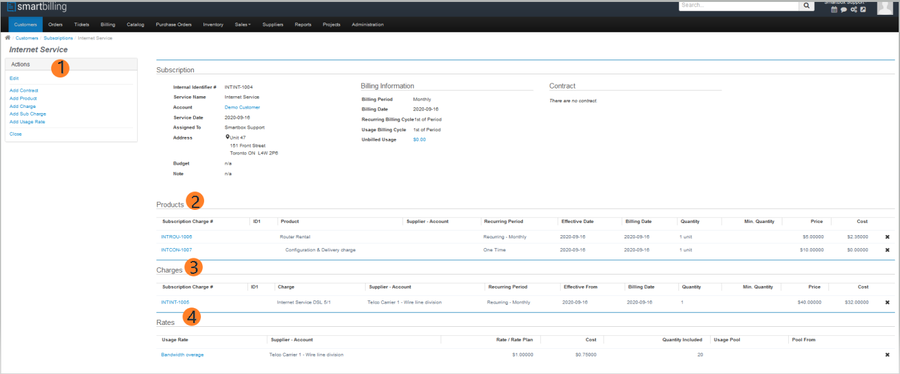
Note that only Charges, Products and Usage Rates defined within the Service upon which a Subscription is based can be added to the Subscription.
¶ Products & Misc.Charges
Companies sell products or services to customers. In the subscription economy, services are attached to subscriptions, while products are usually one off services that are charged as a one off cost to the customer. See the example below.
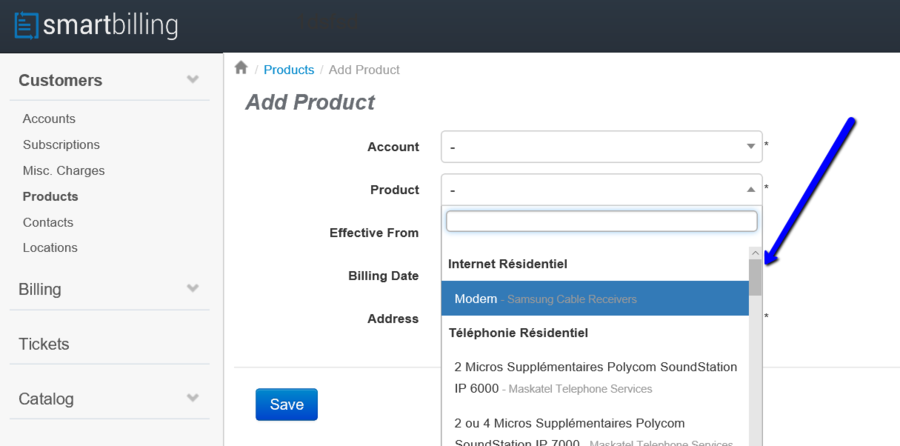
In order to add a product to a customer, the product needs to be created in the Catalog previously. Same happens for Adding Charges. Those need to be created as part of the Catalog, and then added at Customer > Charge level. See below for illustration purposes.
